Oracle Forms can be run using local network but if you want to access your oracle forms application via globally on internet, you have to use public IP and DMZ Hosting configuration.
A public IP address is an IP address that can be accessed over the Internet. Like postal address used to deliver a postal mail to your home, a public IP address is the globally unique IP address assigned to a computing device. Your public IP address can be found at What is my IP Address page. Private IP address, on the other hand, is used to assign computers within your private space without letting them directly expose to the Internet. For example, if you have multiple computers within your home you may want to use private IP addresses to address each computer within your home. In this scenario, your router gets the public IP address, and each of the computers, tablets and smartphones connected to your router (via wired or wifi) gets a private IP address from your router via DHCP protocol.
Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA) is the organization responsible for registering IP address ranges to organizations and Internet Service Providers (ISPs). To allow organizations to freely assign private IP addresses, the Network Information Center (InterNIC) has reserved certain address blocks for private use. The following IP blocks are reserved for private IP addresses.
What is public IP address?
A public IP address is the address that is assigned to a computing device to allow direct access over the Internet. A web server, email server and any server device directly accessible from the Internet are candidate for a public IP address. A public IP address is globally unique, and can only be assigned to a unique device.
What is private IP address?
A private IP address is the address space allocated by InterNIC to allow organizations to create their own private network. There are three IP blocks (1 class A, 1 class B and 1 class C) reserved for a private use. The computers, tablets and smartphones sitting behind your home, and the personal computers within an organizations are usually assigned private IP addresses. A network printer residing in your home is assigned a private address so that only your family can print to your local printer.
When a computer is assigned a private IP address, the local devices see this computer via it's private IP address. However, the devices residing outside of your local network cannot directly communicate via the private IP address, but uses your router's public IP address to communicate. To allow direct access to a local device which is assigned a private IP address, a Network Address Translator (NAT) should be used.
What is a DMZ
A DMZ (demilitarized zone) on a home router refers to a DMZ Host. Strictly speaking, this is not a true DMZ. A home router DMZ host is a host on the internal network that has all UDP and TCP ports open and exposed, except those ports otherwise forwarded. They are often used a simple method to forward all ports to another firewall/NAT device.
How to configure DMZ Host
Step 1: Login to the management page
Open the web browser and type the IP address of the device in the address bar
(default is 192.168.1.1 / 192.168.0.1 / 192.168.0.254).
The default username and password are both admin. Click OK to log into the device.
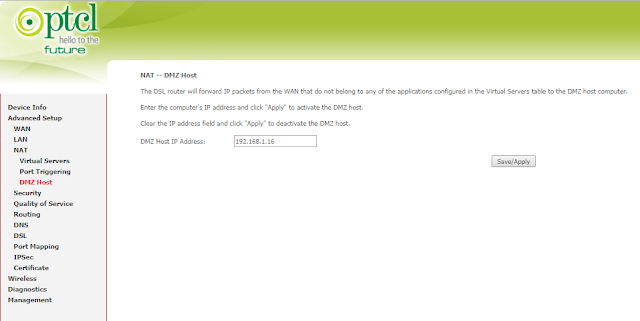
Step 2: Configure the DMZ
Click: Advance Setup> NAT> DMZ Host. Input the IP of host device (here takes 192.168.1.16 as example), then click Save
Note: Power cycle/reboot your router for you settings to take effect.
No comments:
Post a Comment